Juno BSX - The self-powerd operating hours counter with live status detection
Automatacally records when your machine is active - and when it’s not.
Self-powered, contactless, and robust – for industry & construction sites.

Innovative and robust measurement technology for electric machines
The system measures the electric field without contact, stores all data internally, and functions fully energy-autonomous – requiring no external power, cabling, or maintenance.
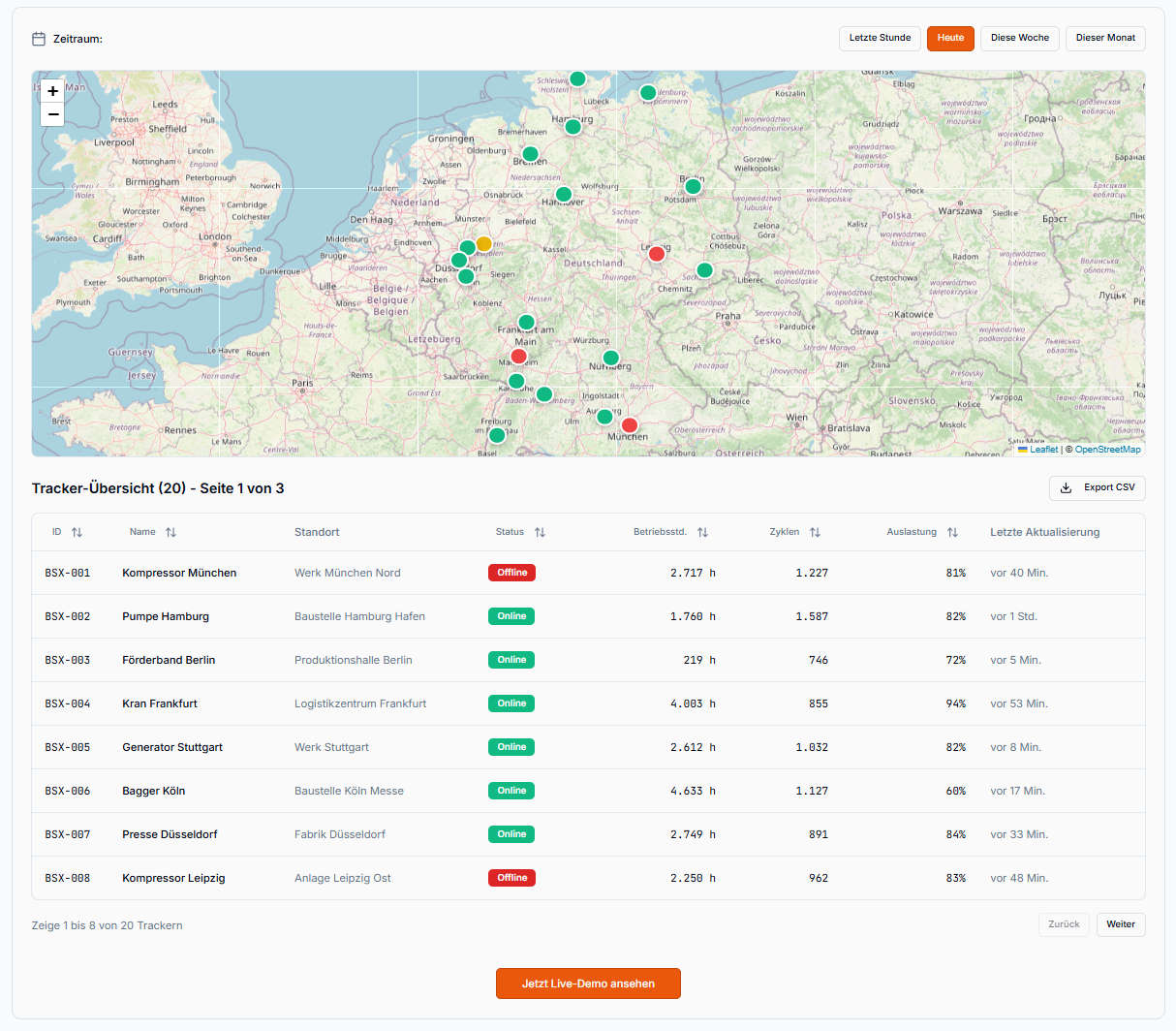
Live-Status and run time at a glance
In the web dashboard, you can instantly see which machines are active, how long they’ve been running, and when maintenance is due.
Downtimes are detected automatically – ideal for fleet or plant monitoring.
The sensors are also equipped with GPS and can transmit location data.
No control over machine runtimes or operating status?
Unscheduled downtimes, unused capacity, or incomplete maintenance data?
With Juno BSX, you can monitor at any time which machines are active – and their total runtime.

Transparency , Efficiency, Control
No more guessing. No more wasted downtime.
Core Features
Real-time detection
Continuous monitoring instantly recognizes status changes – for example, when a machine switches on or off.
Energy autonomous
Battery-powered, maintenance-free design enables multi-year operation with ultra-low-power consumption.
Precise runtime tracking
An integrated counter logs operating hours via the electric field and stores the values permanently.
Multi Connectivity
Available with common IoT protocols: Cellular (NB-IoT and LTE-Cat-M1), LoRaWAN, or mioty.
Industries and applications
Agri & Municipal
![]()
Construction
Production
![]()
Sustainability & ISO integration:
ISO 50001 & ISO 14001
How an operating hour counter contributes to ISO 50001 compliance
The Juno BSX actively supports environmental and energy management systems in accordance with ISO 50001 and ISO 14001.
By precisely recording machine operating times, it enables the derivation of energy-related key figures, allocation of consumption, and identification of energy efficiency potentials.
Records the runtimes of individual machines or systems.
When combined with power data (kW), it provides machine-specific energy consumption.
This enables load analysis, energy efficiency comparison, and CO₂ tracking per unit of use.
Example:
A machine runs 12 h/day and draws 7.5 kW → 90 kWh/day.Reducing the runtime by 10 % saves 9 kWh per day – demonstrable with Juno BSX data.
Supporting ISO 14001 compliance
Tracks environmental impacts through key metrics on resource usage and emissions.
Runtime data helps companies pinpoint energy- and resource-intensive processes and calculate machine-level CO₂ emissions.
Combined with energy meters, Juno BSX can act as a trigger for energy logging:
“When a machine is running → start energy metering.”
Juno BSX provides transparency in:
- Energy consumption per machine or system component
- CO₂ emissions per operating hour
- Resource usage in the production process
Practical benefits for ISO-compliant companies
- Transparent machine usage as a basis for energy and environmental indicators
- Identification of energy-saving potentials
- Proof of improvements
Sentinum DataHub – Central data management
All sensor data in one place.
The Sentinum DataHub receives, stores, and distributes data from your Juno BSX trackers via standardized interfaces.
The DataHub serves as the central link between your Juno BSX sensors and existing IT systems – from ERP and MES to custom dashboards and analytics platforms.
MQTT Protocol
Real-time transmission with minimal latency for time-critical applications.
REST API
Flexible, HTTP-based API for seamless integration.
Data persistence
Automatic storage and historical logging of all sensor data.
Encrypted transmission
TLS/SSL-secured communication for maximum data security.
FAQ
Technical functionality
The operating hour counter uses changes in the magnetic field that occur during the operation of a machine or device to automatically detect active phases.
A 3-axis magnetic field sensor is used, which measures the local magnetic field continuously or at defined intervals.
When a characteristic magnetic field change is detected – for example, when a motor starts, parts rotate, or current flows nearby – the electronics interpret this as an “active operating state.”
These active periods are time-integrated to calculate the cumulative operating hours.
Applications and use cases
The use of the Juno BSX operating hour counter requires that the monitored device or machine generates an electrical or magnetic field. This typically occurs during the operation of motors, alternators, generators, or other electromagnetic components.
The device detects characteristic field changes caused by current flow, commutation, or alternating magnetic fields and uses these signals to record operating or switching states without contact.
Typical applications are found in electromechanical drives such as DC, AC, or BLDC motors.
Here, magnetic field changes resulting from rotation or commutation are detected, enabling stable signal acquisition.
Alternators and generators also produce distinctive magnetic variations during power generation, allowing detection of charging or operating states.
Fans, pumps, or compressors can be reliably monitored for runtime and maintenance intervals through the field changes of their motors.
Electromagnetic clutches can likewise be detected when activated, providing precise counting of switching cycles.
In the area of electromagnetic actuators, the range of applications is equally broad:
Solenoid valves, relays, and contactors generate measurable magnetic fields or pulses when activated, enabling accurate detection of switching times and cycles.
Linear solenoids and actuators can also be monitored based on field changes during movement — for example, in industrial automation or automotive systems.
In power generation and distribution, Juno BSX enables contactless runtime and operation monitoring of alternators, transformers, or inverters by detecting stray or induced magnetic fields under load.
Beyond industrial use, the system is also suitable for household and commercial appliances.
Power tools, vacuum cleaners, blowers, or heaters can be analyzed in terms of operating time and frequency of use, while in induction heating systems or refrigeration units, both compressor and fan fields can be monitored simultaneously.
In vehicle and machinery manufacturing, the operating hour counter can monitor starter-generators, electric drives, hydraulic pumps, conveyors, or drive rollers.
By detecting magnetic field variations or current flow, it enables precise runtime and maintenance analysis — even under harsh environmental conditions.
Finally, there are additional applications in renewable energy systems:
In solar tracking systems or auxiliary drives of wind turbines (e.g., yaw or pitch drives), the device records magnetic field changes caused by motor movement, allowing detailed operating-hour logging.
Magnetic bearings and magnetic brakes can also be monitored, as their activation produces characteristic magnetic field changes.
Typische Anwendungen finden sich bei elektromechanischen Antrieben wie Gleich-, Wechsel- oder bürstenlosen Gleichstrommotoren (DC/AC/BLDC). Hier werden Magnetfeldänderungen durch das Drehfeld oder die Kommutierung detektiert, was eine stabile Signalerfassung ermöglicht. Auch Lichtmaschinen und Generatoren erzeugen durch das magnetische Wechselfeld während der Stromerzeugung eindeutige Signale, die eine Erkennung des Lade- oder Betriebszustands erlauben. Ventilatoren, Pumpen oder Kompressoren lassen sich über die Feldänderungen ihrer Motoren zuverlässig hinsichtlich Laufzeit und Wartungsintervallen überwachen. Ebenso können elektromagnetische Kupplungen durch ihr Magnetfeld bei Aktivierung erfasst werden, was eine präzise Zählung der Schaltzyklen ermöglicht.
Im Bereich der elektromagnetischen Aktoren ist die Anwendung ebenfalls vielfältig: Magnetventile, Relais oder Schütze erzeugen bei Aktivierung ein messbares Magnetfeld oder einen Feldimpuls, wodurch Schaltzeiten und Zyklen exakt erfasst werden können. Auch Hubmagnete und Linearantriebe lassen sich anhand ihrer Feldänderung beim Bewegen überwachen – etwa in der Industrieautomation oder Fahrzeugtechnik.
In der Energieerzeugung und -verteilung ermöglicht der Juno BSX die kontaktlose Laufzeit- und Betriebsüberwachung von Lichtmaschinen, Transformatoren oder Wechselrichtern, indem er magnetische Streufelder oder induzierte Felder bei Last erkennt.
Darüber hinaus eignet sich das System auch für Haushalts- und Industriegeräte. Elektrowerkzeuge, Staubsauger, Gebläse oder Heizlüfter lassen sich hinsichtlich ihrer Laufzeit oder Nutzungshäufigkeit auswerten, während bei Induktionsheizungen und Kühlaggregaten eine kombinierte Überwachung von Kompressor- und Lüfterfeldern möglich ist.
Im Fahrzeug- und Maschinenbau kann der Betriebsstundenzähler zur Überwachung von Startergeneratoren, E-Maschinen, Hydraulikpumpen, Förderbändern oder Antriebsrollen eingesetzt werden. Hier ermöglicht die Detektion von Magnetfeldänderungen oder Stromflüssen eine präzise Betriebsdauer- und Wartungsanalyse – auch unter rauen Umgebungsbedingungen.
Schließlich finden sich weitere Einsatzmöglichkeiten in erneuerbaren Energiesystemen: Bei Solarnachführsystemen oder Windkraft-Nebenantrieben (z. B. Yaw- oder Pitch-Systemen) erfasst das Gerät Magnetfeldänderungen durch Motorbewegungen und erlaubt so ein detailliertes Betriebsstunden-Logging. Auch Magnetlager und Magnetbremsen können überwacht werden, da ihre Aktivierung mit charakteristischen Feldänderungen verbunden ist.
Installation notes
Recommended mounting location
-
Placement:Mount directly on the motor housing or close to the windings, preferably at an unshielded position (not directly behind a steel plate).
-
Avoid interference:Do not place the sensor on or next to live power cables to prevent disturbances from external electromagnetic sources.
-
Mechanical stability:Ensure stable, low-vibration mounting and protect the sensor from direct heat radiation.
-
Orientation:The sensor measures in 3D – orientation is not critical, but one axis should ideally point radially toward the motor field to capture the strongest signal.
-
Mounting method:For example, use a screw, clip, or double-sided adhesive pad with thermal insulation.
The strength and range of the detectable field depend on several factors:
-
Motor type (DC, BLDC, asynchronous)
-
Housing material (magnetic or non-magnetic)
-
Power level and current flow
-
Shielding / installation environment
-
Position of windings and magnets
Sources of interference
The magnetic field of a motor decreases exponentially—or more precisely, according to 1/r³ (dipole field)—with increasing distance.
This means that even a few centimeters of spacing significantly reduce the motor’s signal strength, while more distant sources become barely measurable. As a result:
-
When the sensor is mounted close to the target motor (e.g., <5 cm), the influence of other machines is practically negligible.
-
If the sensor is placed further away (>10 cm), the useful signal can weaken rapidly, and stronger external fields (e.g., from large motors or transformers) may overlap or interfere.


